APEMS, ??, Understanding APEMS in Depth: Applications, Purpose, and Evolving Meaning Systems
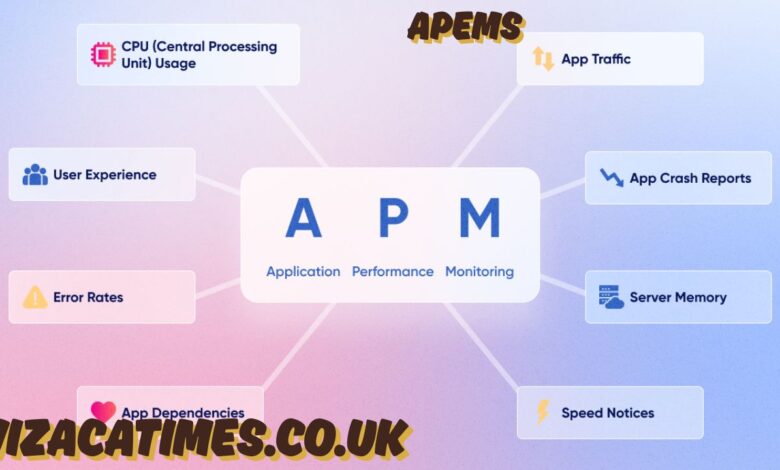
Introduction to APEMS: What Does APEMS Stand For??
The term APEMS is often encountered in multiple contexts, leading to some confusion. Depending on the industry or discipline, APEMS may refer to a system, methodology, or even an organization. Broadly, it stands for Applications, Purpose, Evolving Meaning Systems, but other variants exist in education, technology, environmental management, and public policy. This article explores the multi-layered meanings behind APEMS, examining how the concept applies in modern systems thinking, organizational frameworks, and socio-environmental domains.
The Conceptual Basis of APEMS
At its core, APEMS encapsulates a framework where applications are designed with a specific purpose in mind, guided by evolving meaning systems. These evolving systems can include changes in cultural understanding, technology, environmental conditions, or institutional values. APEMS is not a static model; it’s dynamic and adaptive, reflecting the continuous flux of the real world.
The idea here is that every application—whether it’s a software, policy, program, or educational tool—must not be examined in isolation but in the context of its evolving meaning. Why was it developed? What purpose does it serve now? How has its use or interpretation changed over time? APEMS invites these critical questions.
APEMS in Education: Adaptive Pedagogical and Evaluation Management Systems
In education, APEMS has gained relevance as a framework for Adaptive Pedagogical and Evaluation Management Systems. These systems are designed to support continuous learning and dynamic evaluation processes. They consider:
- The application of learning tools and digital platforms
- The purpose of assessments and their alignment with learning outcomes
- The evolving nature of student needs and institutional missions
For example, in modern classrooms, learning is no longer about rote memorization but about creating meaning through interaction and discovery. APEMS encourages educators to design curricula that evolve with technological advancement and societal shifts.
APEMS in Environmental and Public Policy Systems
In environmental and public policy contexts, APEMS often refers to Applied Policy and Environmental Monitoring Systems. This interpretation of APEMS is essential for sustainable governance and includes:
- The application of monitoring tools like GIS and remote sensors
- The purpose of protecting ecological and human health
- The evolving interpretations of sustainability and public good
For instance, a forest conservation program may have originally focused solely on biodiversity, but evolving meaning systems now include community livelihoods, climate mitigation, and Indigenous rights. APEMS as a tool helps policymakers incorporate these new meanings into monitoring and strategy frameworks.
APEMS in Business and Organizational Design
APEMS can also relate to Agile Performance Evaluation and Management Systems in business settings. In this domain, the system focuses on:
- Applying tools for team performance tracking
- The purpose of achieving strategic alignment
- The evolving expectations of stakeholders, customers, and employees
Traditional models of organizational evaluation often fail to account for rapidly changing markets. APEMS encourages agile frameworks where performance metrics evolve along with company values and consumer behavior.
For example, companies today are expected to be sustainable and socially responsible. APEMS helps organizations track performance not just in profit but also in social impact, ethical governance, and employee well-being.
The Role of Purpose in APEMS
A central feature of the APEMS framework is purpose. Without a clearly defined purpose, applications risk becoming outdated or irrelevant. Purpose defines the direction of any project or system within the APEMS framework and ensures that:
- Resources are allocated efficiently
- Stakeholders remain engaged
- Outcomes align with core values
Whether designing a new app, developing public health interventions, or revising an academic curriculum, the purpose must evolve with societal needs. This is where APEMS becomes a living system—constantly adapting and renewing its internal goals.
Evolving Meaning Systems in Practice
The term evolving meaning systems refers to the dynamic interpretations, values, and symbols that define how humans understand the world. These meanings are shaped by:
- Technological innovations
- Cultural transformations
- Political shifts
- Scientific discoveries
For instance, the meaning of “security” has evolved from national defense to include cyber protection and mental well-being. Similarly, “education” has expanded from formal schooling to lifelong learning facilitated by mobile apps, online platforms, and community-based instruction.
APEMS uses these evolving meanings as a guidepost. By recognizing that the meanings of key concepts change, APEMS encourages flexibility, reflection, andinclusive decision-making.
Case Example: Applying APEMS to Urban Planning
Let’s explore a concrete example: urban transportation. A city decides to revamp its public transport. Here’s how APEMS would approach this:
- Applications: New electric buses, bike-sharing platforms, real-time data tracking apps.
- Purpose: Reduce pollution, improve accessibility, enhance public health.
- Evolving Meaning Systems: Today’s urban dwellers value sustainability, convenience, and affordability. Future values might emphasize personal space (post-pandemic trends) or digital integration (AI in transport).
This APEMS-based approach ensures the transport system remains responsive and aligned with changing public expectations and technological capabilities.
Limitations and Challenges of APEMS
While powerful, the APEMS model is not without its challenges:
- Complexity: Managing constantly evolving meanings can be overwhelming.
- Resistance to Change: Organizations and institutions may resist adaptive models due to tradition or bureaucracy.
- Data Dependency: Monitoring systems require robust data, which may not be readily available in all regions or sectors.
Still, with the right commitment, these obstacles can be overcome. APEMS promotes transparency, inclusivity, and adaptability—qualities that are increasingly vital in the modern world.
Future Prospects for APEMS
As digital transformation, global collaboration, and sustainability goals become central to all disciplines, APEMS is likely to gain wider acceptance. From corporate boardrooms to municipal governments and research institutes, the demand for systems that can adapt, align with purpose, and incorporate evolving societal meanings will only grow.
Moreover, the rise of AI-driven decision-making, climate adaptation, and inclusive development models will further underscore the need for APEMS-based approaches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is APEMS in simple terms?
A: APEMS stands for Applications, Purpose, and Evolving Meaning Systems. It is a framework used to evaluate and design systems that can adapt over time based on changing values and needs.
Q2: Where is APEMS used?
A: APEMS is used in education, public policy, environmental science, business strategy, and organizational design. It helps ensure systems remain relevant and purposeful.
Q3: Why are evolving meaning systems important in APEMS?
A: Because societal values, technologies, and expectations change over time. Systems must evolve too, or they risk becoming obsolete or misaligned.
Q4: Can small businesses use the APEMS framework?
A: Absolutely. APEMS helps small businesses clarify their goals, adapt to market changes, and remain aligned with customer values.
Q5: Is APEMS the same as traditional evaluation methods?
A: No. Traditional methods often assess static metrics. APEMS is dynamic, reflecting ongoing changes in purpose and meaning.
Conclusion: APEMS as a Path Toward Purpose-Driven Adaptability
The APEMS model—whether understood as an educational system, policy tool, or organizational strategy—invites us to consider the deeper connections between purpose, application, and evolving societal meaning. In a fast-changing world where what we value today might shift tomorrow, APEMS provides a powerful lens for continuous learning, ethical leadership, and sustainable action. Whether you’re a policymaker, business leader, educator, or student, embracing the principles of APEMS means staying not just relevant—but responsible.
Also read : Anjali Kari, ??, A Journey of Passion and Purpose


