Thermal Resource Sales,?? Understanding the Market, Demand, and Future Growth Potential

Thermal Resource Sales,?? Market Demand and Emerging Dynamics
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, thermal resource sales play a significant role in shaping how nations meet their power needs while transitioning towards cleaner alternatives. While renewables are at the forefront of global discussions, thermal resources—including coal, oil, natural gas, and geothermal energy—continue to dominate energy consumption across many regions. This article explores everything you need to know about thermal resource sales,?? their driving factors, associated markets, and the trends influencing future growth.
Understanding Thermal Resource Sales,??

At its core, thermal resource sales refer to the commercial transactions and market activities related to the supply and distribution of heat-producing energy resources. These resources primarily include:
- Fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas)
- Geothermal energy
- Bioenergy resources (such as biomass)
These resources are used in power generation, industrial manufacturing, home heating, and even agriculture. The sales involve producers, utilities, governments, and intermediaries that manage supply chains and logistics from source to consumption.
Major Types of Thermal Resources Driving Sales
Coal Sales:
Coal remains a dominant thermal resource in countries such as China, India, and South Africa. Despite environmental concerns, the affordability and infrastructure built around coal keep it an essential part of thermal resource sales in emerging economies.
Natural Gas Sales:
Natural gas has emerged as a cleaner-burning alternative to coal. It is heavily traded internationally via pipelines and as liquefied natural gas (LNG). Nations such as the U.S., Qatar, and Russia are among the top exporters, and the demand continues to surge globally, especially in Europe and Asia.
Oil-Based Thermal Sales:
Crude oil and its refined products (like diesel and heating oil) are still widely used in heating, power backup systems, and industrial operations. Oil-based thermal resource sales remain significant in regions with limited renewable integration.
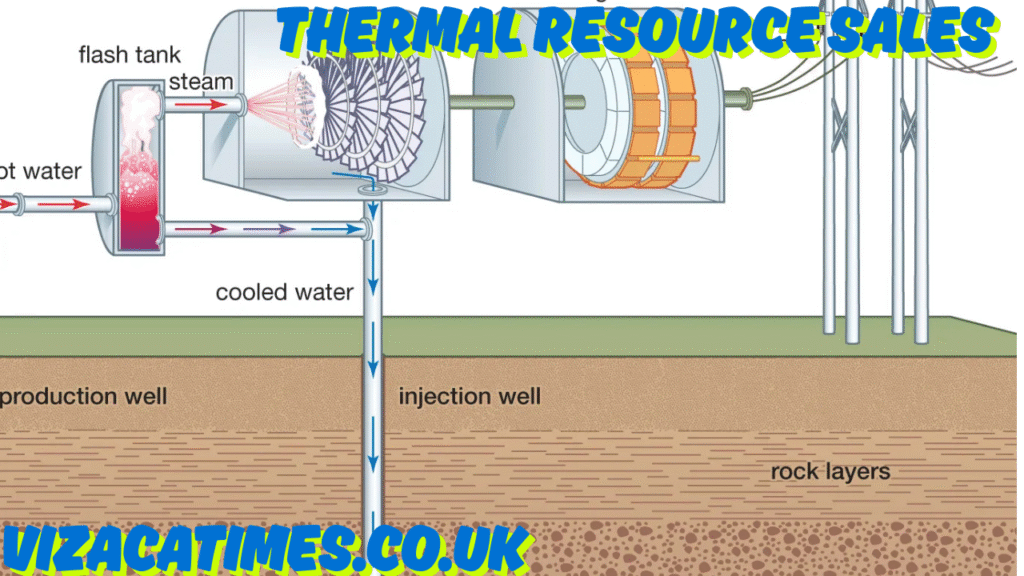
Geothermal Resource Sales:
Though less widely adopted, geothermal energy is a reliable thermal resource in geologically favorable areas. Countries like Iceland and the Philippines have integrated geothermal power into their national grids, contributing to both domestic consumption and export.
Who Are the Key Players in Thermal Resource Sales?
Producers and Extractors: These include oil companies, coal mining firms, and natural gas extractors. Their role is to locate, extract, and prepare the thermal resources for sale.
Traders and Brokers: Specialized trading firms handle transactions between producers and buyers. They monitor market prices, demand forecasts, and regulations to ensure profitable trades.
Governments and State-Owned Enterprises: In many countries, governments either directly control thermal resource production or regulate it heavily. Taxes, subsidies, and export controls play a crucial role in influencing sales.
End-Users and Utilities: Power plants, manufacturing companies, and commercial buyers purchase large quantities of thermal resources for operational use, especially in electricity generation.
Thermal Resource Sales in the Global Market
The market for thermal resource sales is global and interconnected. An economic shift in one region, like reduced coal demand in Europe, can redirect supply to growing markets in Southeast Asia. Prices are influenced by:
- Geopolitical events
- Environmental policies
- Weather-related factors (e.g., cold winters, heatwaves)
- Technological advancements
The transition to cleaner energy doesn’t necessarily mean a drop in thermal resource demand. Instead, it reshapes the demand dynamics. For instance, natural gas has become a bridging fuel in many countries as they move from coal to renewables.
Thermal Resource Sales?? Economic Impact
Thermal resources significantly contribute to national GDPs, especially in resource-rich countries. For example:
- Export revenues from thermal coal and gas fund infrastructure projects.
- Thermal resource taxation boosts public budgets.
- Job creation spans from mining and refining to logistics and power production.
However, there are also environmental costs associated with thermal resource extraction and usage. These include air pollution, water usage, and greenhouse gas emissions, which bring regulations and carbon pricing into the economic equation.
Challenges Facing the Thermal Resource Sales Industry
Regulatory Pressure:
Many countries have implemented carbon caps, emissions trading schemes, and environmental taxes that affect the profitability and logistics of thermal resource sales.
Transition to Renewables:
While renewables are not yet fully capable of replacing thermal energy, the push toward solar, wind, and hydroelectric power creates a growing competition. This impacts long-term contracts and investment interest in fossil-based thermal resources.
Infrastructure Aging:
Pipelines, refineries, and power stations in some regions are outdated. This leads to higher maintenance costs and increased vulnerability to outages and inefficiency.
Market Volatility:
Prices for oil, coal, and gas can fluctuate dramatically based on international incidents, natural disasters, or diplomatic relations—making long-term planning challenging for suppliers and buyers.
Future Outlook for Thermal Resource Sales??
Despite global efforts toward clean energy, the thermal resource sales market is expected to remain relevant for decades. Some trends pointing to this include:
- Energy security concerns: Countries are ensuring stable supplies of thermal resources during times of renewable shortfalls.
- Growth in developing economies: As more nations industrialize, demand for affordable and readily available thermal energy rises.
- Technological innovation: Carbon capture, storage, and cleaner combustion methods may extend the viability of fossil-based thermal resources.
- Hybrid energy models: Integration of geothermal or bioenergy into mixed-resource grids creates new sales channels.
Thus, the market is not shrinking—it is evolving.
Regional Spotlight: Where Thermal Resource Sales Are Booming
- Asia-Pacific: India, China, and Southeast Asian nations are rapidly expanding coal and gas infrastructure to meet soaring electricity demand.
- Middle East: With large natural gas reserves, the Gulf nations continue to drive LNG exports.
- Africa: Countries like Mozambique and Nigeria are becoming key players in gas sales, while coal and oil still dominate local energy usage.
- Europe: While transitioning, some Eastern European countries continue to rely on coal and gas, especially during winter months.
- Latin America: Geothermal energy is rising, especially in countries within the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What exactly are thermal resource sales??
Thermal resource sales refer to the buying and selling of energy resources that generate heat, such as coal, oil, natural gas, and geothermal energy, which are used for electricity generation, heating, and industrial processes.
Q2: Are thermal resources being phased out?
Not entirely. While some countries are reducing their reliance on coal, natural gas and geothermal resources continue to grow in demand as transitional or complementary energy sources.
Q3: What is the most traded thermal resource today?
Natural gas, particularly in the form of LNG, has become one of the most actively traded thermal resources globally, due to its cleaner combustion and versatility.
Q4: How do thermal resource sales affect climate policy?
They are a central focus of climate policy, as fossil fuels contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Regulations often aim to reduce sales or encourage cleaner alternatives, affecting market dynamics.
Q5: Will geothermal energy overtake other thermal resources?
Geothermal energy has potential in specific regions, but due to geological limitations, it’s unlikely to fully replace fossil-based thermal resources on a global scale in the near future.
Final Thoughts on Thermal Resource Sales,??
The future of thermal resource sales is neither fixed nor fading. As global energy demands shift, the landscape of this market adapts—driven by innovation, policy, economics, and necessity. Understanding the balance between demand, environmental impact, and geopolitical strategy is essential for anyone involved in this crucial sector. Whether fossil-based or renewable in origin, thermal resources will continue to fuel industries, homes, and economies for decades to come—making the discussion around thermal resource sales?? more relevant than ever.
Also read : Izideal, ?? – Exploring the Concept, Platform, and Questions Around “Izideal”